Dizziness
Dizziness is a nonspecific term that usually means one of the following three:
Rotational
or
Spinning sensation

VERTIGO



Lightheadedness
And
Impending Fainting

Near fainting
Presyncope


Impaired Balance
And
Gait
Disequilibrium



VERTIGO

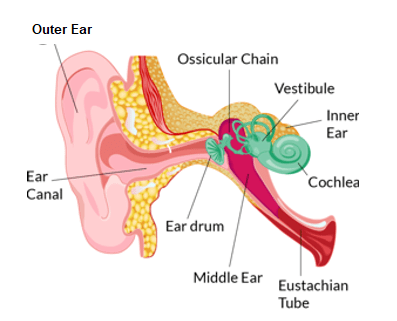
Peripheral Vertigo is caused by inner ear dysfunction sending false movement sensation or augmented signals when the head is moving.
Common symptoms associated with peripheral vertigo:
- Nausea and vomiting most of the time
- Ear ringing or Tinnitus sometimes
- Nystagmus (eyes moving and bouncing for seconds when trying to look at things) is always present
- Hearing loss often present
- Patient appears ill and can be disabled by the vertigo
- Most of the causes are benign
- Usually sudden in onset
Peripheral Vertigo Common Causes
- Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo:
Most common cause, Female > male
Caused by displacement of crystal in the inner ear Transient and recurring. Treated with Eply repositioning maneuvers - Vestibular Neuronitis complicates viral respiratory infections , causes more severe symptoms than BPPV and last longer
- Labyrinthitis presents similar to vestibular neuronitis + hearing loss
- Meniere disease is caused by increased pressure in the inner ear causing episodic attacks of Vertigo and tinnitus associated with gradual hearing decline
- Acoustic neuroma
Central Vertigo is caused brain dysfunction causing misinterpretation of signals coming from the balance organs (the eyes, ears & feet).
Central vertigo has the following properties:
- May cause nausea or vomiting
- Ear ringing or tinnitus is very rare
- They usually have no nystagmus or may have vertical nystagmus (eyes bouncing up and down not side to side)
- No hearing loss (rare)
- Does not appear very ill
- Most of the causes are non minor
- Onset is usually mild
Central vertigo common causes
- Stroke
- Brain Trauma
- Brain infections
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Alcoholism
- Migraine
Every patient with acute Vertigo should be evaluated in urgent care or ER to determine the cause (central or peripheral). If central cause is diagnosed then ER visit is a must.
Presyncope and Impending Fainting
Transient decrease in brain blood flow leading to the feeling of impending passing out. If the decrease in blood flow is significant then syncope (passing out) occurs.
Normal brain blood flow requires 3 essential components to work in harmony:
- Good Heart Muscle & valves to pump up blood at the needed Pace
- Good Blood Volume
- Good heart and blood vessels Nerves to control the function of the heart pump and the blood vessels tension to provide the right brain perfusion
Breakdown in any of the 3 components can lead to dizziness and may lead to fainting.
Nerve Mediated (most common cause)
- Vasovagal reaction (slowing in the heart beat and BP drop triggered by Vagus nerve stimulation by fear or stress.
- Vagus nerve can be stimulated by cough or urination
- Warning signs include nausea and sweating Fatigue and weakness may follow
- Chronic diseases can lead to nerve dysfunction and poor BP control reflexes leading to dizziness like with Diabetes and Alcoholism
- Medications can affect the nerve function
Blood Volume decrease causes Orthostatic Hypotension)
(Third most common cause)
- Dehydration
- Acute blood loss from any cause
Heart causes (second most common cause)
- Heart attacks leading to pump weakness or failure
- Very rapid or slow heart beat leading to ineffective pumping of blood
- Tight heart valves
- Thick heart ineffective muscle
- Aortic dissection, the main blood vessel is failing
- Heart tamponade ( fluid in the sac around the heart)
- Pulmonary Embolism (Lung blood clot)
Dizziness & Disequilibrium
Disequilibrium refers to a sensation of imbalance or unsteadiness that is primarily experienced during positional changes, standing or walking and it is relieved with sitting or lying down.
Disequilibrium results usually from multiple factors in an elderly person:
- Decreased vision
- Decreased hearing
- Muscle weakness or atrophy
- Joints (knees and hips) disease
- Decreased sensation of position in feet (neuropathy)
- Brain atrophy
