Diabetes Mellitus
Definitions:
|
Test |
Normal |
Pre Diabetes |
Diabetes |
|
Fasting Glucose |
<100mg/dl |
100-124mg/dl |
>125mg/dl |
|
2 Hrs Glucose Tolerance |
<140mg/dl |
140-199mg/dl |
>200mg/dl |
|
Hemoglobin A1c |
<5.7% |
5.7-6.4% |
>6.5% |
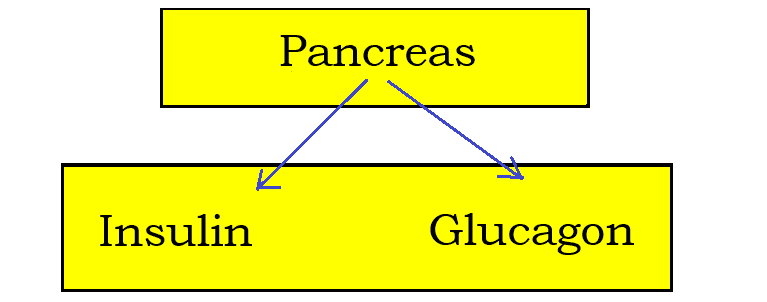
Insulin Function in Healthy Person:
The overall simplified action of insulin is to promote the uptake of nutrients in the feeding state and to promote the release of nutrients in the fasting state.
Feeding State
Insulin

Glucagon

Fasting State
Insulin

Glucagon

Effects on Liver
- Increase in Glycogen synthesis
- Increase Glucose use
- Increase Glucose transport
- Stop Glucose release from liver
Liver
Effects on Liver
- Increase in Glycogen breakdown and release of Glucose to circulation
- Activation of new Glucose synthesis and release
Effects on Fat Cells
- Increase in Glucose uptake
- Increase in Triglycerides uptake
- Increase in fat synthesis
Fat Cells
Effect on Fat Cells
- Increase in Fat Breakdown
- Fatty Acids Oxidation
Effects on Muscles
- Increase Glucose uptake
- Increase Amnio Acids transport
- Increase in Protein Synthesis
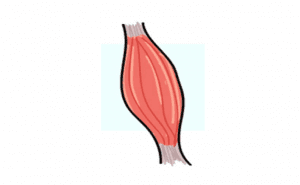
Muscle
Effects on Muscles
- Stops Glucose uptake by Muscles
- Increase in protein Breakdown
Simplified Classification of Diabetes Mellitus
Type I ( 5-10% )

- Usually Young and Thin patient
- The Beta cells in the Pancreas are destroyed by:
- In Type I A: there is self destruction by auto-antibodies facilitated by genetic factors
- In Type I B: No antibodies are found in the blood and the B cell destruction is caused by infection, drugs, neoplasm and chronic pancreas inflammation from any cause
- There is Total loss of insulin production

Total Insulin Depletion
Type II ( 90-95% )

- Usually Middle aged or older & overweight
- There is slow decrease in the Pancreas ability to make and release Insulin associated with insulin action resistance made worse by obesity, muscle loss and inactivity

Decreased & Less effective Insulin
Organ
Chronic Changes
Acute Complications
Eye
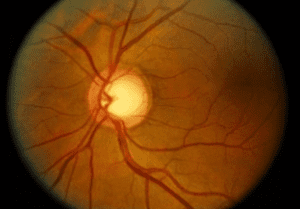
- Diabetic retinopathy is the leading cause for blindness
- Its severity and progression depends on the duration and the level of sugar control, the presence of uncontrolled hypertension or hypercholestrolemia
- It can cause:
- A- Proliferative vascular changes in the vitrous
- B- Non proliferative changes including micro aneurysm, bleeding and exudate
- Intraocular hemorrhage
- Retinal detachment
- Vision loss
Nerves
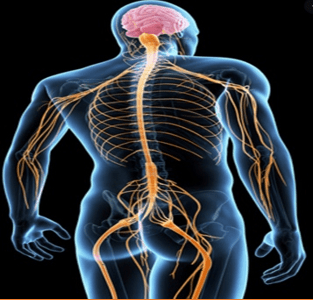
- Diabetic Neuropathy usually affects hands and feet
- It causes pain, burning and tingling
- If larger nerve are affected it may cause loss of position sensation, vibration and light touch
- Autonomic Neuropathy can cause Gastrointestinal (Gatstroparesis or Diarrhea), urinary.
(Bladder and Erectile dysfunction) heart symptoms (dizziness)
- Intractable nerve pain
- Dizziness and other autonomic nerve dysfunction symptoms
- It can mask a heart attack
Heart
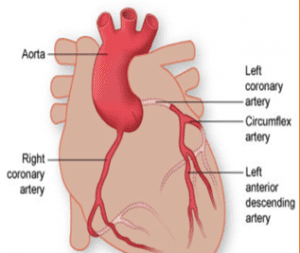
- Diabetes is an independent risk factor for Coronary Heart disease
- It increases the risk for atherosclerosis and narrowing of the coronary arteries
- Chest pain can be atypical or masked by diseased nerves
- Chest pain/Angina
- Heart Attack
Kidney
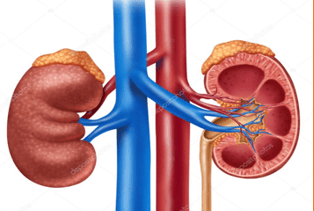
- Diabetic Nephropathy is the leading cause of end stage kidney disease
- Uncontrolled hypertension is another important cause and works in harmony with Diabetes in damaging kidneys
- Kidney failure and need for dialysis
- Heart Attack
Vessels & Circulation
The Major burden of long standing uncontrolled Diabetes is the development of micro vascular disease leading to Eye, Kidney and Nerve disease.
In addition it affects the Coronary and Cerebral arteries
Any vital organ sudden decrease in circulation leading to major presentation like stroke or heart attack
It may cause legs poor circulation and Diabetic Foot Ulcer
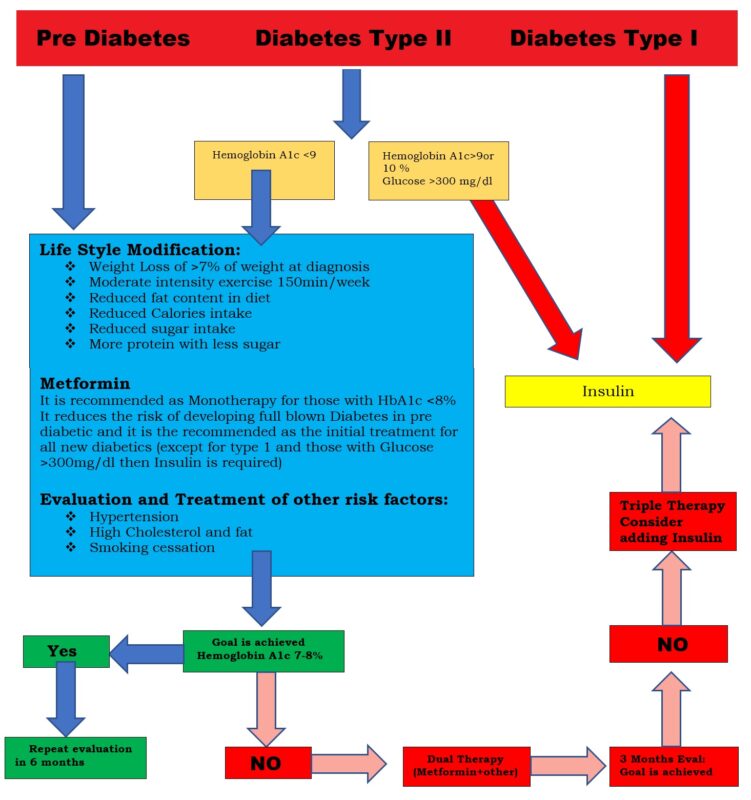
Management of Diabetes Mellitus
Contact Medical Care 1 in Ypsilanti. Learn more about our urgent care services. Go back to Education page.