Hypertension Definitions
Definitions (Guidelines updated in 2017):
Blood Pressure Classification | Systolic Pressure | Diastolic Pressure |
Normal | <120 | And <80 |
Elevated Blood Pressure | 120-129 | <80 |
Stage I Hypertension | 130-139 | Or 80-89 |
Stage II Hypertension | >140 | Or >90 |
White Coat Hypertension = Elevated Blood pressure during office visits only and normal at home.
Masked Hypertension = Normal Blood Pressure at the office and high at home
Malignant Hypertension = Elevated Blood Pressure leading to vital organs damage
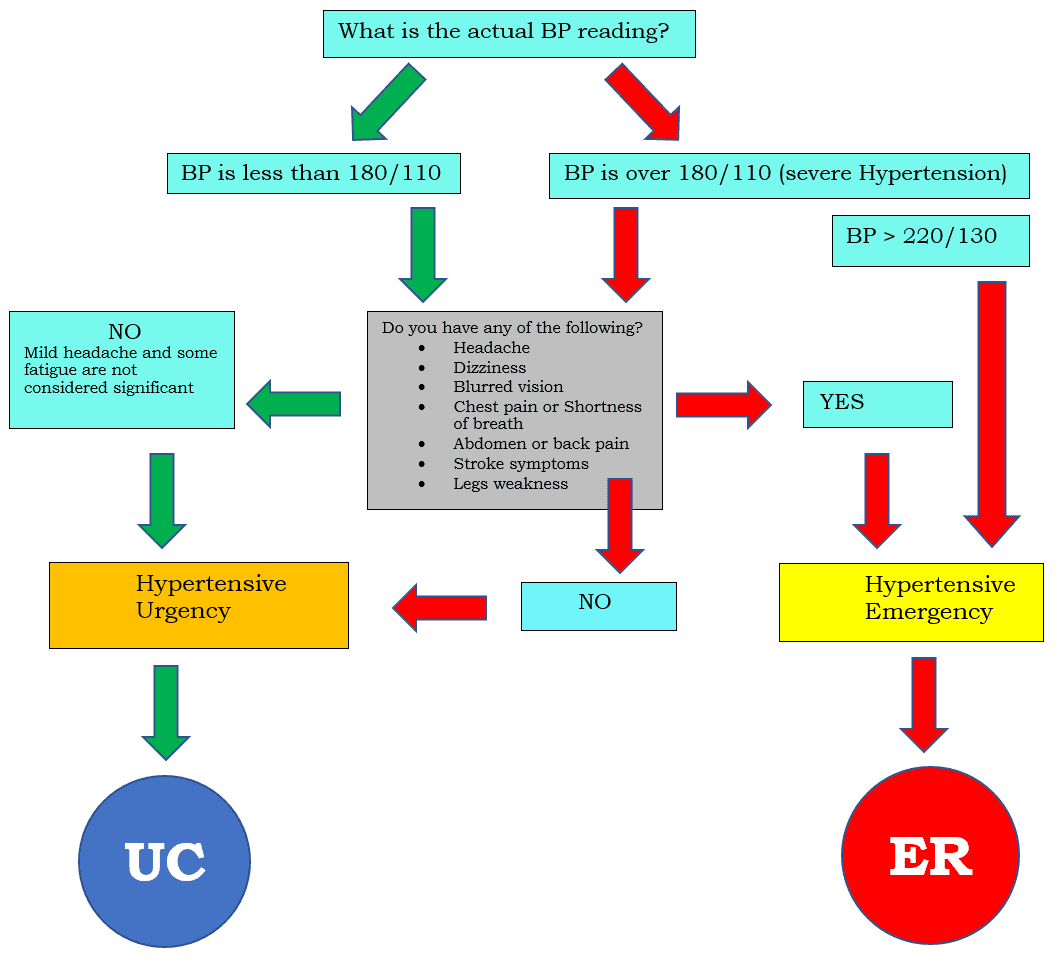
Hypertensive Urgency = Elevated blood pressure without any symptom

Hypertensive Emergency = Elevated blood pressure with symptoms related to organ dysfunction caused by the abnormal blood pressure for example High blood pressure with headache or chest pain

Classification of Hypertension According to Cause
Primary Hypertension (90%) = Elevated blood pressure due to hardening of the arteries and genetic factors
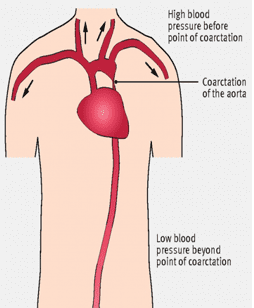
Secondary Hypertension (10%) = Elevated blood pressure caused by either kidney disease , Excessive hormones secretion, Obstructive Sleep apnea or Coarctation of Aorta
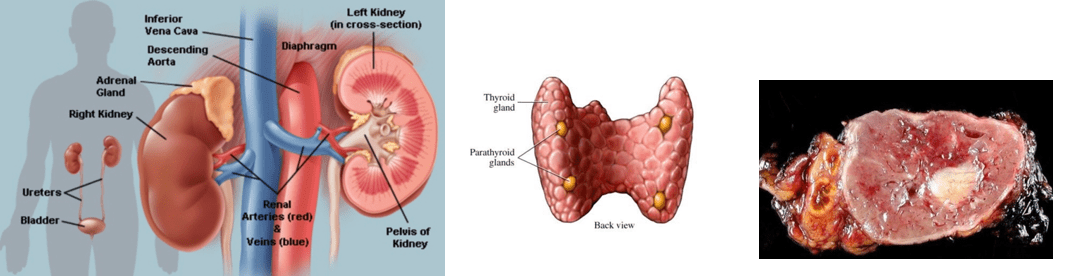
- Kidney disease and kidney artery stenosis (narrowing)
- Thyroid over or under production of hormones
- Parathyroid glands over production of hormones
- Adrenal Gland Tumors (Pheochromocytoma)
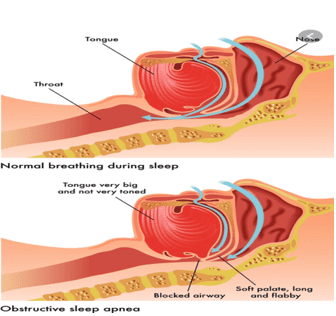
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea
- Coarctation of Aorta
Results of Untreated Sustained Hypertension on Vital Organs
Organ
Chronic Changes
Acute Complications
Eye
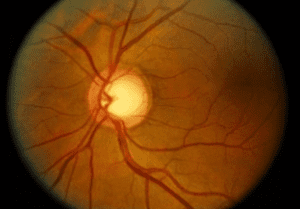
Retinopathy
Optic Neuropathy
May lead to gradual visual lossPapilledema (swelling of the optic disc)
May lead to sudden vision loss and blindness
Brain
Decreased brain circulation with increased risk of mini stroke and dementia
May lead to gradual brain function deterioration
Brain bleed
Seizure
Altered mental status
May lead to major stroke or fatality
Heart
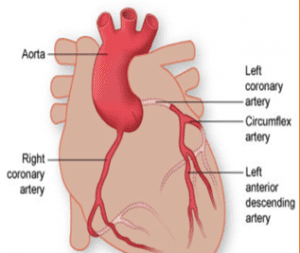
Heart muscle thickness
(Hypertrophy) and weakness (Heart Failure)
May lead to chest pain and shortness of breath
Heart Attack and/or Failure
May cause chest pain.
If not fatal it can reduce the heart pump strength and lead to chronic heart failure
Kidney
Gradual kidney scarring and loss of function
May lead to symptoms of gradual slowly progressive kidney failure
Acute kidney injury and failure
May need Dialysis
Meduim and Large Blood Vessels

Peripheral Vascular disease and poor circulation
Weakness,Pain, numbness and intermittent claudication
Aortic Aneurysm and dissection
May cause acute chest and back pain or abdomen pain
May be fatal
***Please notify your physician of your BP reading for appointment and evaluation
Hypertension Initial Evaluation Goals
The Goal of the primary care office evaluation is:
- To rule out secondary (curable) cause of hypertension (Kidney and hormones)
- To assess and treat other modifiable causes of vascular diseases like high cholesterol and Diabetes
- To assess the presence and severity of hypertension related organ disease if any
Initial Testing Recommended for New Onset Hypertension
- EKG
- Blood Testing: CBC, Metabolic Panel, estimated GFR, Lipid Panel, Fasting Blood Sugar and Thyroid function
- Urinalysis with Microscopic exam and Urine Albumin
- More specific testing can be recommended if the initial evaluation is suspicious for secondary hypertension (Kidney disease or Hormone excess
Overview of Hypertension Treatment
- Weight Reduction
- Reduce dietary salt
- DASH diet (Fruits, Vegetables, Low fat dairy, Whole grain, Legumes, Low saturated fat, low Sodium, High Potassium, Magnesium and Calcium
- Increase Potassium
- Daily exercise
- Elderly Not in nursing home —> BP <130/80
- Non Elderly —> BP < 130/80
- Diabetes —> BP < 130/80
- Kidney Disease —> BP < 130/80
- You may start with any of the following:
- Calcium Channel Blocker
- Ace Inhibitor or ARB
- Chlorthalidone
- 2 medications are recommended for stage 2 hypertension
- Re-evaluation is recommended at 4 weeks interval to assess response to medical treatment and need for dose adjustment
- In Black you may start with either Calcium Channel Blocker or Thiazides Diuretic
- Other classes of antihypertensives can be used in specific situations
- Resistant hypertension should raise suspicion for secondary causes
Medical Care One is an urgent care and Walk-in clinic in Ypsilanti. Urgent Care Online: We offer Telemedicine. Visit Urgent Care Near You – No Appointment Necessary. COVID-19 safety info.